I’m sure you have ever come across the term type checking, either static or dynamic type checking while reading a textbook about your favorite programming language or during the late afternoon programming lectures and you probably didn’t fully understand what it meant.
The problem is that some articles have failed to give a clear explanation on what type checking is and the different types but after doing some research and studying of my own, I’ve decided to write a concise article to help you gain a clear understanding of what type checking means and its different types. Type checking verifies and enforces constraints on the type of a variable with the aim of keeping the type errors to a minimum. Type checking ensures that the program is type safe as type errors can occur while the program is running .
Example 1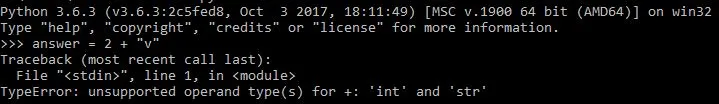
python 3
Above is a python program attempting to add 2 to a string. Adding an integer to a string results into a type error since the expression is not meant to handle multiple data types. As a result, it throws a type error which stops the program from executing.
Under type checking, we have static and dynamic type checking. The key difference between the two is that with static type checking, the type of variable is known at compile time (it checks the type of variable before running) while with dynamic type checking, the type of variable is known at runtime (it checks the type of variable while executing). Compiled programming languages such as C++ and Java are fast because the compiler knows the exact data types used when the variable is initialized which results into optimized code that runs faster and uses less memory. Dynamic type checking results into less optimized code and runtime type error which is likely to occur since it forces runtime checks every time the program executes.
Note: Not all static typed languages are exclusively strongly typed or weakly typed. The same applies to dynamic typed languages.
Strongly typed languages: the type of variable is bound to a specific data type. Most static typed checking languages are strongly typed because the datatype is defined when initializing a variable. Dynamic typed languages are also strongly typed but they use type inference (where the type of variable is determined from the value it holds) to define the datatype of the variable.
Weakly typed languages: their variable type isn’t bound to a specific data type. The variables have a type but its type constraint is lower than that of a strongly typed programming languages.
Example 2
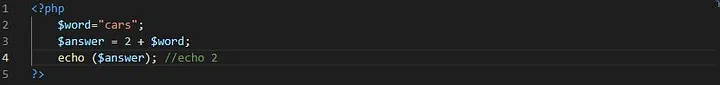
php
The above PHP script adds 2 to a string variable called “ word ” but it outputs 2.
Think of strongly type languages as having a high degree of type safety and weakly typed languages as having a low degree.
Links:
Last modified on 2019-02-18